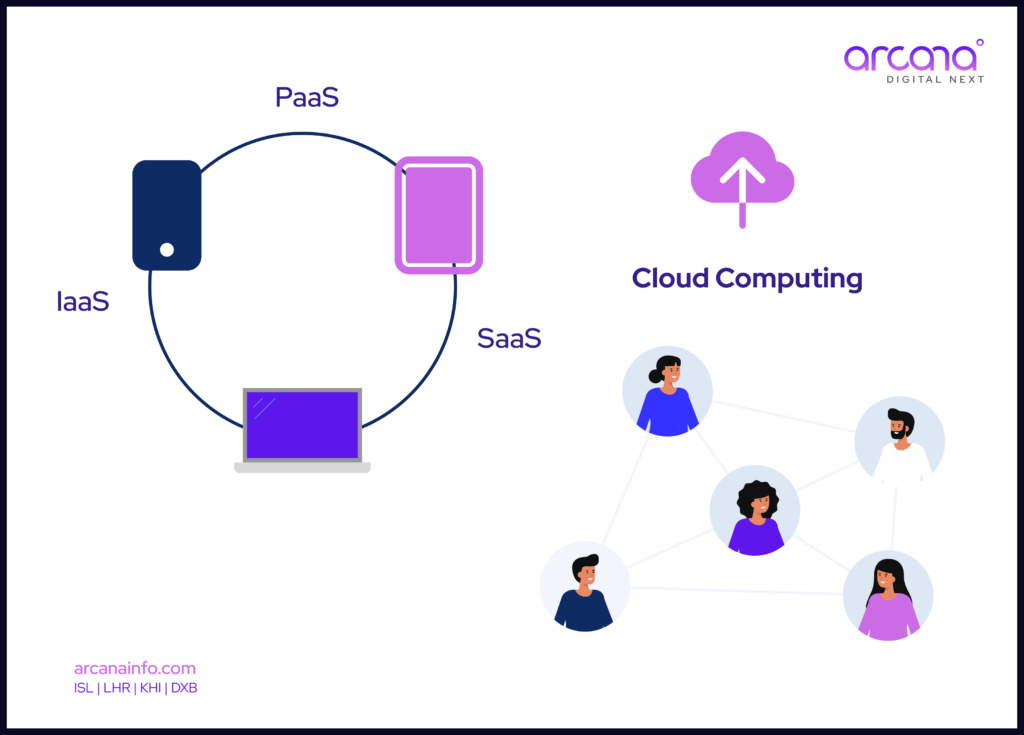
Digital Transformation
We understand that businesses today require more than just technology; they need the right people, with the right skills, at the right time. At Arcana Info, our Virtual Staffing services connect you with highly proficient professionals who seamlessly integrate into your organization, working as an extension of your team under flexible engagement models.